Economic Poster/Calendar Contest
In the Economic Poster Contest, students learn more about the economy in a fun and creative way. Each year, approximately 300 students gain a better understanding of our economic system through their participation in this exciting competition.
Students study a basic economic concept and then use their creativity and art skills to demonstrate their understanding of the concept in a colorful drawing. Teachers submit their entries in both the fall and spring semester, after which 12 winners are selected (each term). Entries are judged on originality, creativity, and accuracy of concept.
For the fall, the 12 state winners’ drawings are featured in a calendar the following year. For the spring, the top 12 entries are each made into posters and hung at the State Capitol for the entire month of April, Financial Literacy Month.
SPRING 2024
ENTRIES DUE
March 8
- PRIZES -
Each winning entry will receive $25 gift card
and a copy of the calendar/poster
ENTRY RULES:
All entries must be original and drawn in color, horizontally on an 8 1/2” x 11” white sheet of paper. Card stock is preferred.
Grades K-8 & 9-12 have different economic concept definitions. Students must choose from the vocabulary terms specified for their grade level (see below).
Entries must illustrate an economic concept from the list provided (see below).
“Double” concepts must both be illustrated.
Each entry should include a completed Entry Form. Tape the entry form to the back of the student’s drawing (one form per drawing.)
The economic concept illustrated must be printed prominently on the drawing, spelled correctly, and written in large lettering.
Entries with misspelled words or drawn only in pen/pencil will be disqualified.
Entries may not be folded.
Entries will be judged on accuracy of content, spelling, creativity, use of color, and artistic ability by grade level
DOWNLOAD CONTEST DETAILS & ENTRY FORM BELOW
SEE ALL OUR WINNERS
ECONOMIC CONCEPT DEFINITIONS
FOR GRADES K-8
ASSETS: Things that have earning power or some other value to their owner.
BUDGET: The amount of money that is available for, required for, or assigned to a particular purpose.
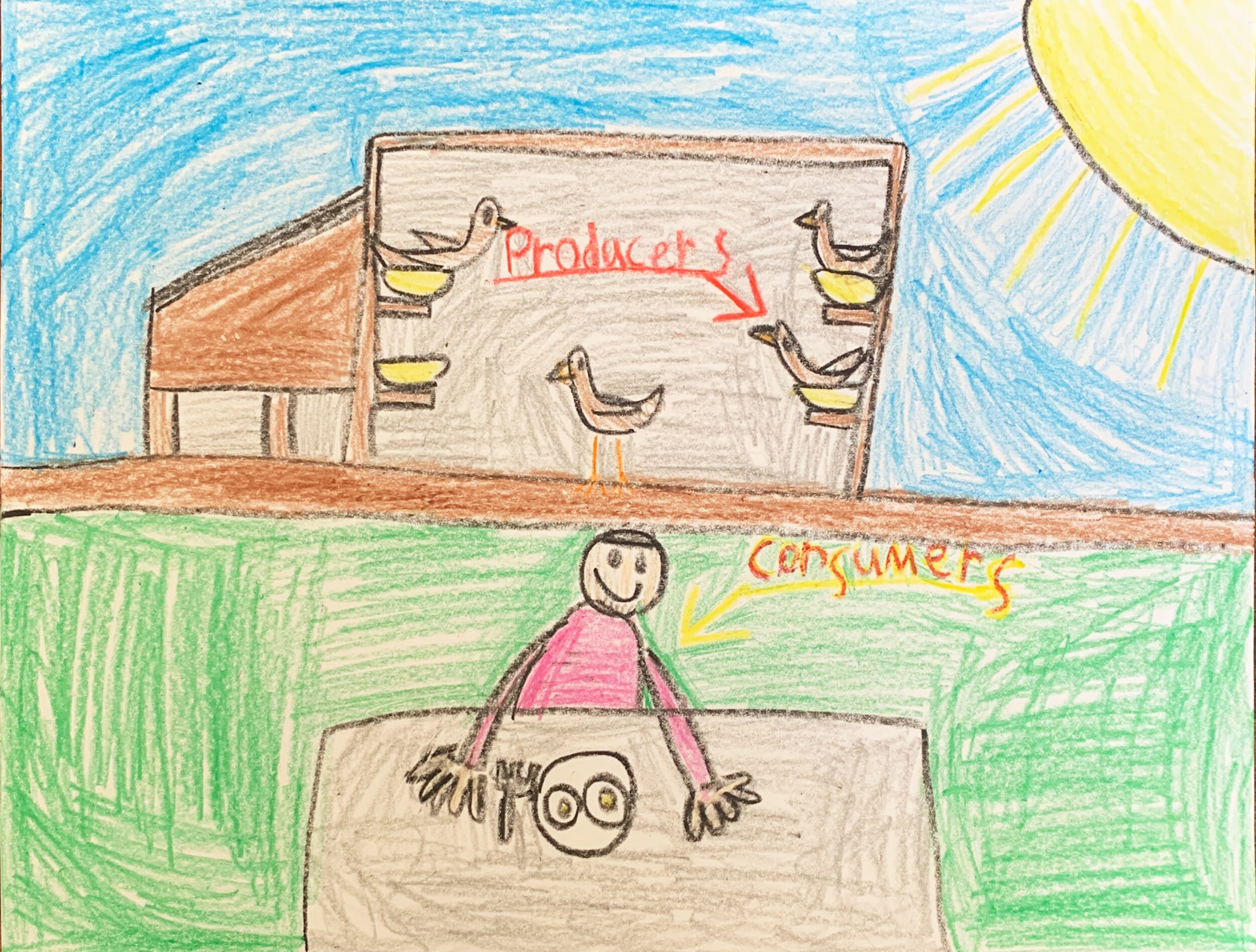
CONSUMERS & PRODUCERS: Consumers are people who buy goods and services. Producers are people who make goods or provide services. Producers supply goods and services and consumers demand them.
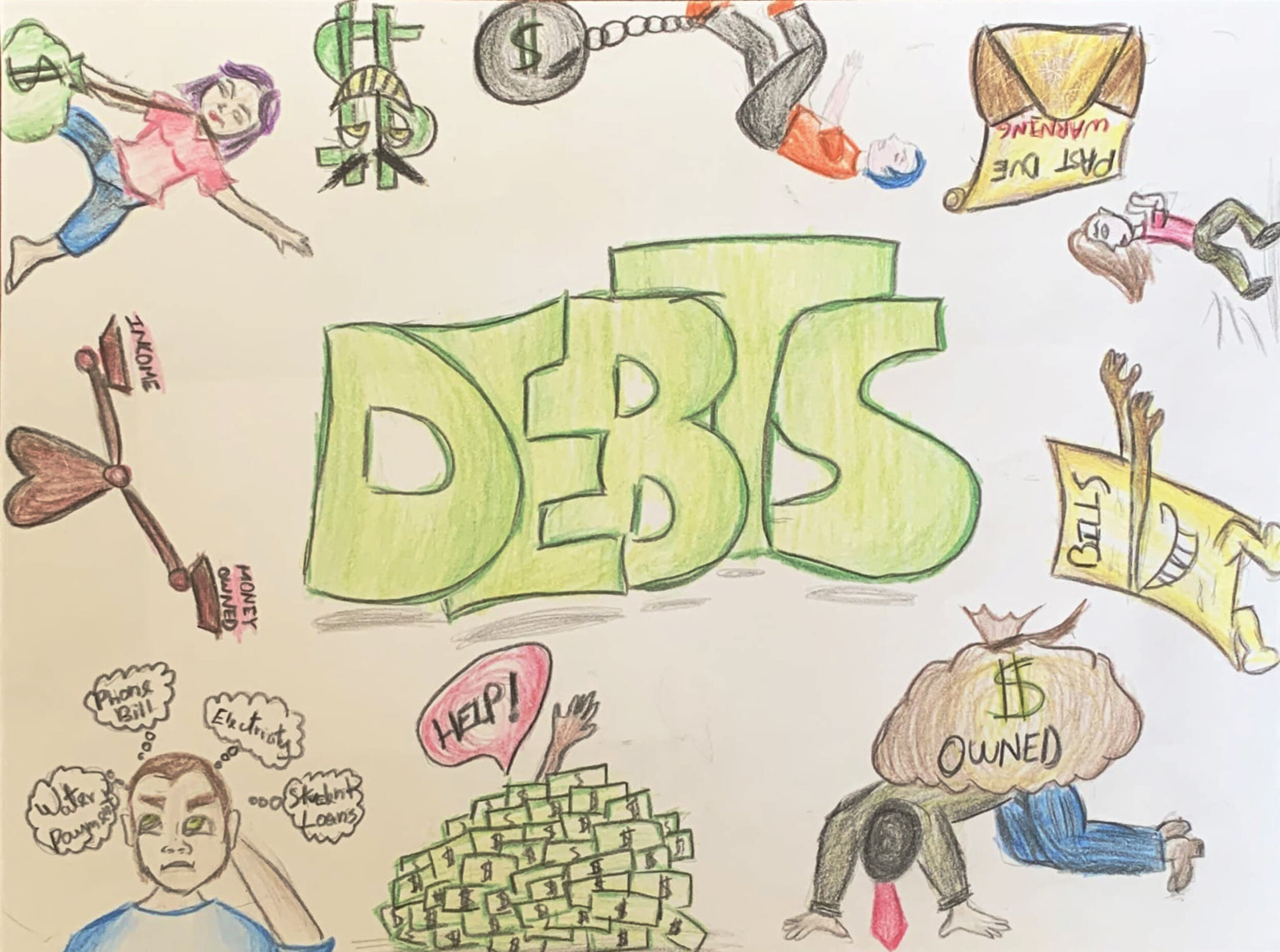
DEBT: Something, typically money, that is owed or due. The state of owing money.
ENTREPRENEUR: An entrepreneur is someone who recognizes an opportunity, marshals the productive resources, and takes the risk to develop or improve a product or start a new business.
GOODS & SERVICES: A Good is an object people want that they can touch or hold. A Service is an action that a person does for someone else. Goods are items you buy such as food, clothing, toys, furniture, and toothpaste. Services are actions such as haircuts, medical check-ups, mail delivery, car repair, and teaching.
INCENTIVES: Factors that motivate and influence the behavior of households and businesses. Prices, profits, and losses act as incentives for participants to take action in a market economy.
SAVINGS: The amount left over when a person’s expenses are subtracted from the amount of disposable income that he or she earns in a given period of time. This occurs when individuals, businesses, or the economy as a whole do not consume all of the current income.
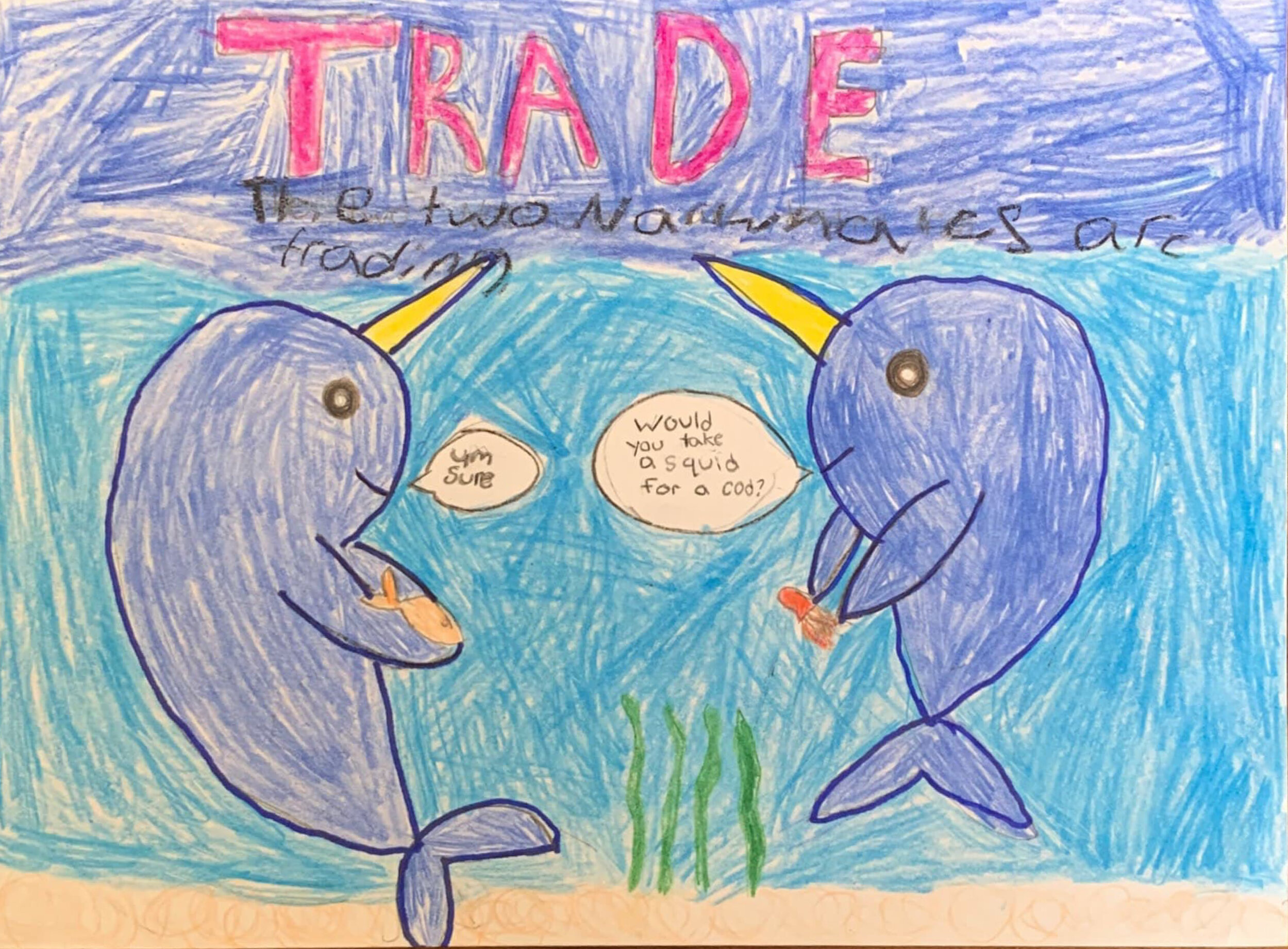
TRADE: The voluntary exchange of goods and services for money or other goods and services. When trade is voluntary, both people benefit. Trade without money is called barter.
FOR GRADES 9-12
DEBT: Something, typically money, that is owed or due. The state of owing money.
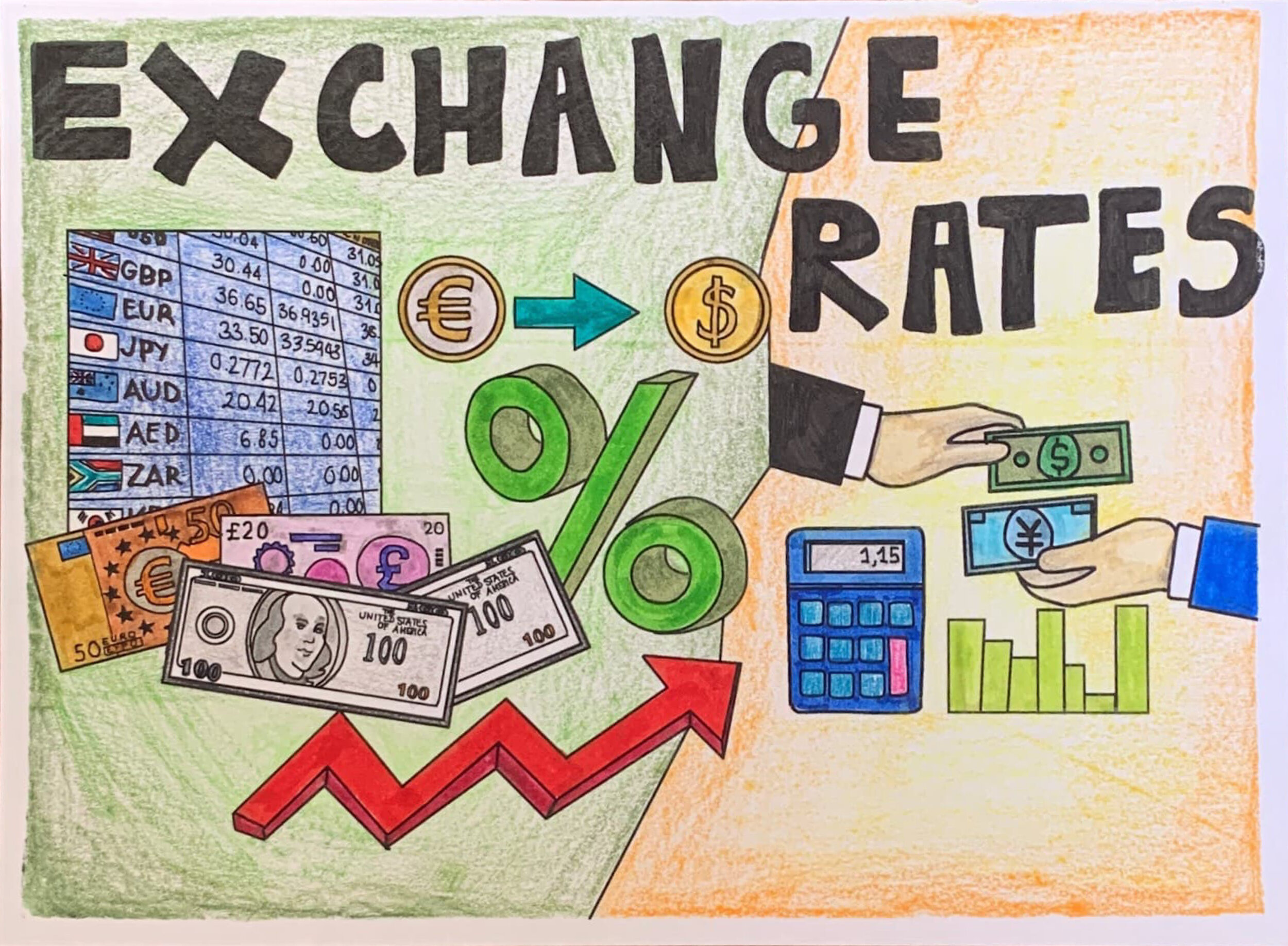
EXCHANGE RATE: The price at which one currency can be converted into another.
EXPORT/IMPORT: Export is the act of sending goods or services to another country for sale. Import is the act of purchasing foreign goods and services.
INFLATION: Rising prices, across the board. Inflation means less bang for your buck, as it erodes the purchasing power of a unit of currency. Inflation usually refers to consumer prices, but it can also be applied to other prices (wholesale goods, wages, assets, and so on). It is usually expressed as an annual percentage rate of change on an index number.
OPPORTUNITY COST: When you make a decision, the most valuable alternative you give up is your opportunity cost. (Opportunity cost is not what you pay to buy something!) There is always an alternative to any decision, so every decision has an opportunity cost.
PRODUCTIVE RESOURCES: All natural resources (land), human resources (labor), and human-made resources (capital) used in the production of goods and services. Note: entry must include human, capital and natural resources.
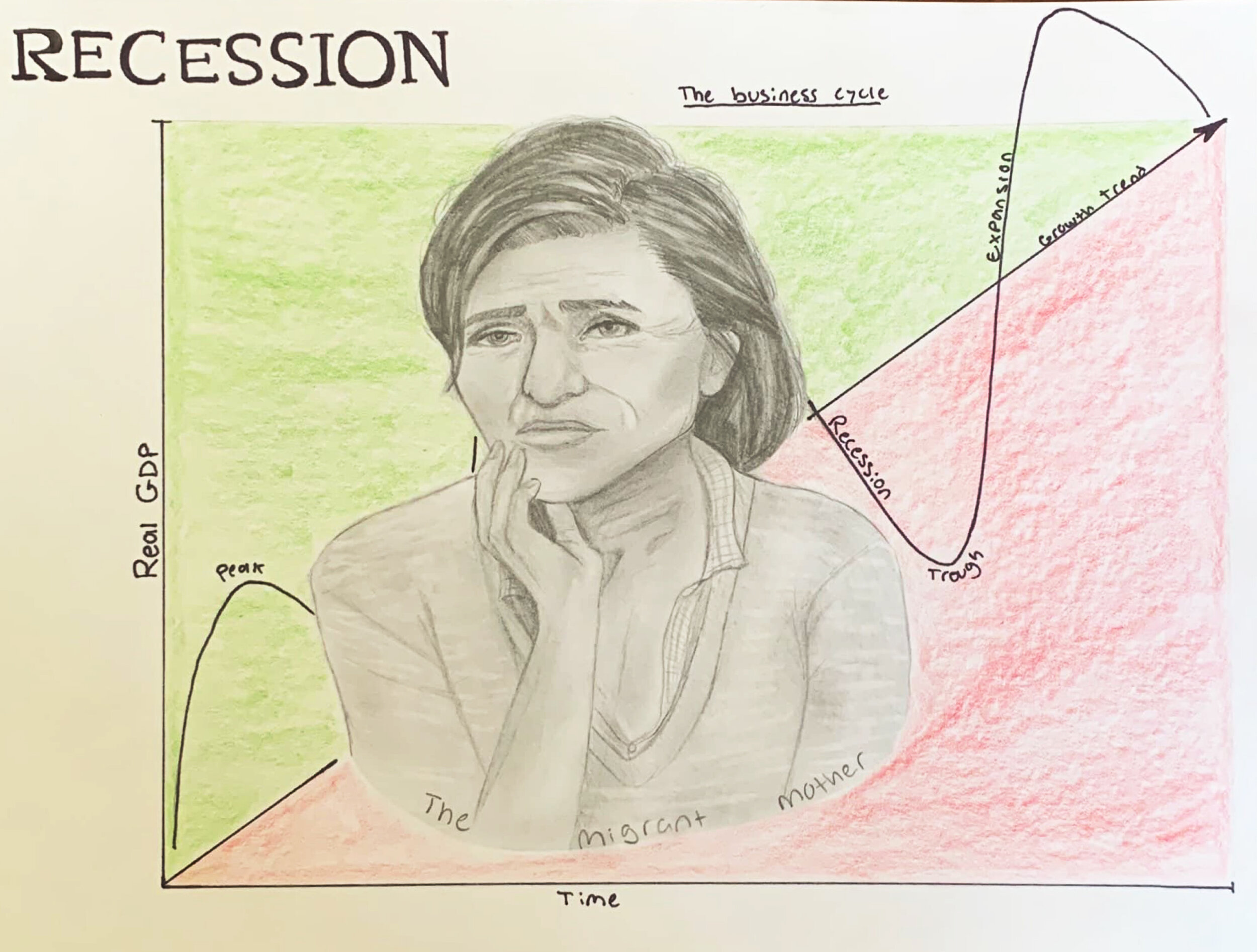
RECESSION: Broadly speaking, a period of slow or negative economic growth, usually accompanied by rising unemployment. A recession is a significant decline in activity across the economy, lasting longer than a few months. Economists have two more precise definitions of a recession. The first is when an economy is growing at less than its long-term trend rate of growth and has spare capacity. The second is two consecutive quarters of falling GDP. It is visible in industrial production, employment, real income and wholesale-retail trade.
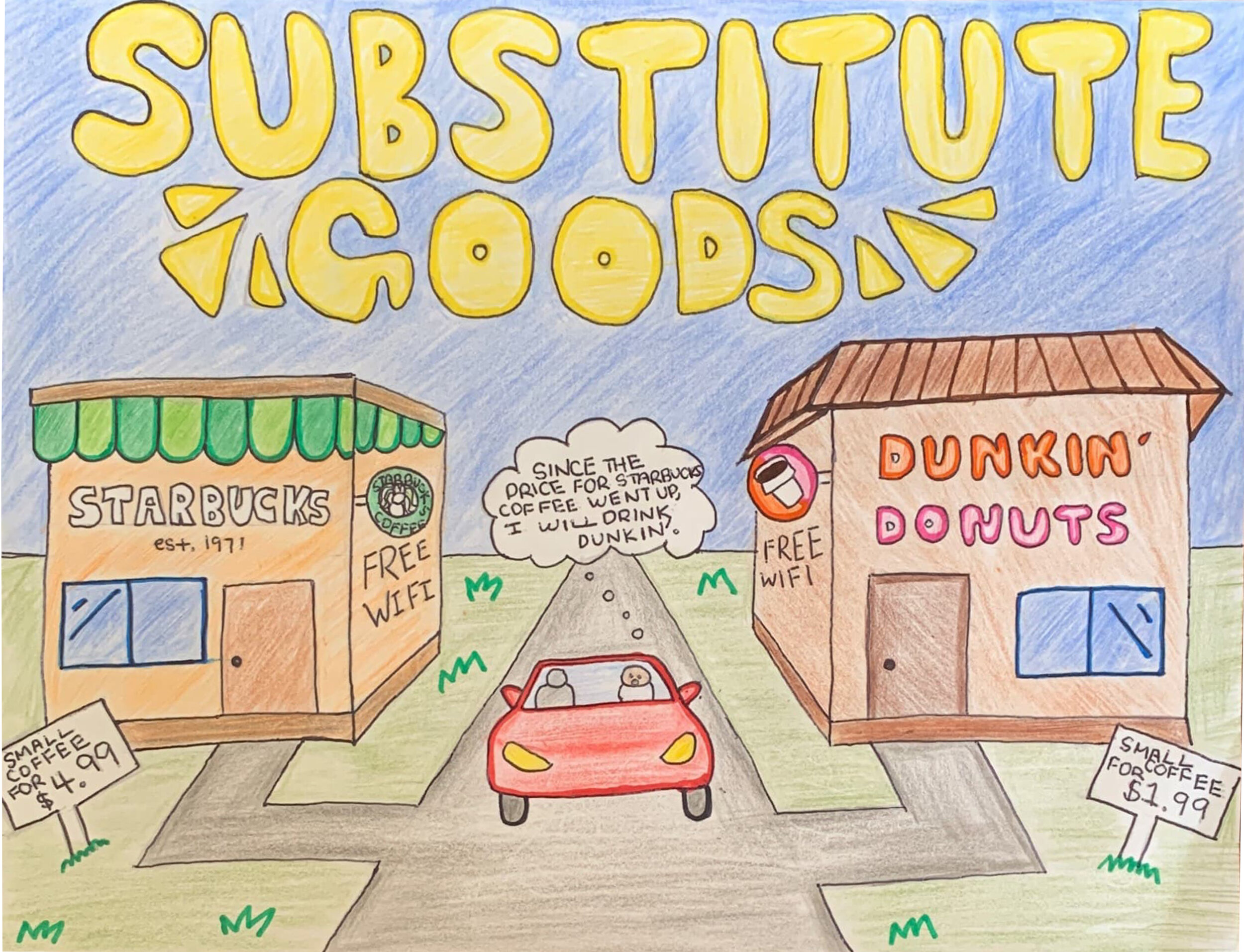
SUBSTITUTE GOODS: Two goods that could be used for the same purpose. If the price of one good increases, then demand for the substitute is likely to rise.
SURPLUS & DEFICIT: A surplus is an excess of income or products (over expenses) in a given period of time. A deficit is the amount by which a resource falls short of a mark, most often used to describe a difference between cash inflows and outflows.